Definition: What is chlorhexidine?
Chlorhexidine - often abbreviated as CHX - is a broad-spectrum antiseptic commonly used in dentistry and medicine. It is known for its strong antimicrobial properties, especially against bacteria, and is used to prevent and treat various infections and oral health problems.
Chlorhexidine is mainly used in antibacterial mouthwashes to treat periodontitis , after dental surgery or to prevent plaque formation. However, the active ingredient can also be contained in gels, creams or toothpaste.
Side effects: Are chlorhexidine mouthwashes bad for the oral flora?
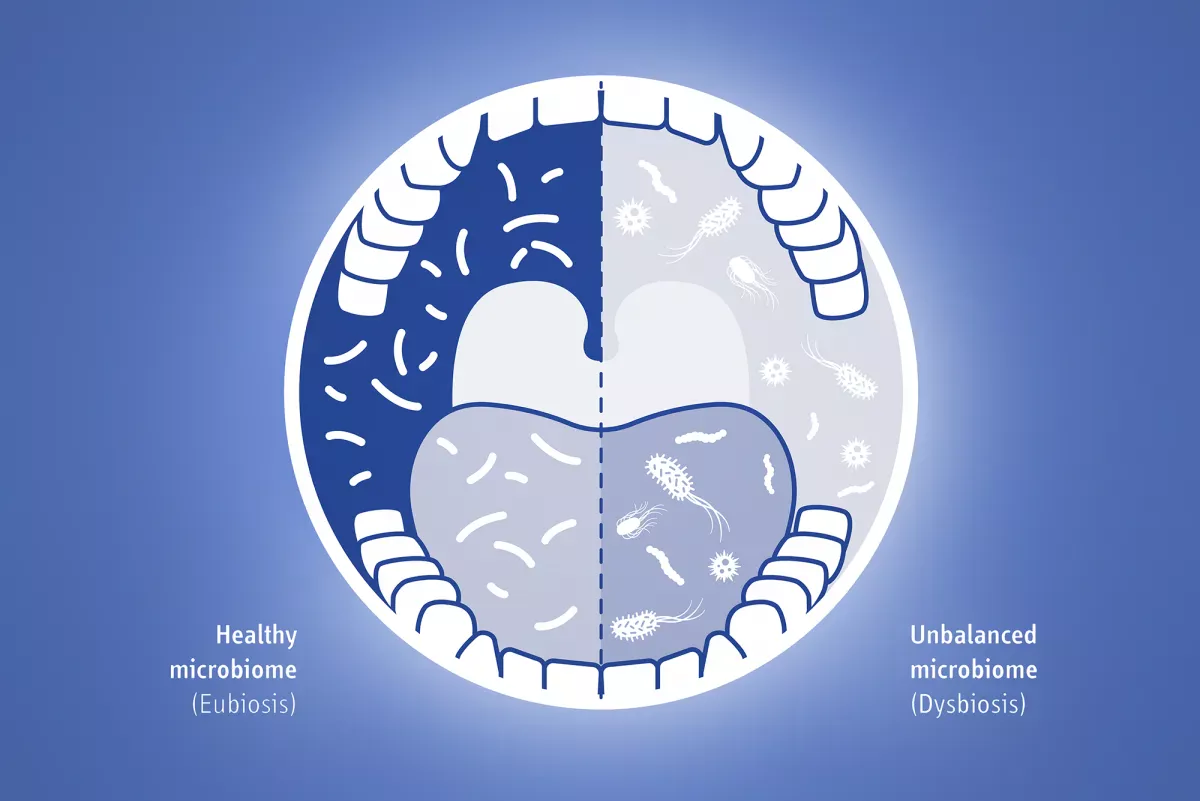
The fact that CHX can eliminate harmful bacteria in the mouth is of course a good thing. However, there is no reason to make a chlorhexidine mouthwash an integral part of your daily dental care routine. Numerous studies have now proven this: Chlorhexidine not only kills harmful bacteria, but also the "good" ones. And this disrupts the oral microbiome - a collection of bacteria, fungi, viruses and other microorganisms that live in our mouths. A balanced microbiome is not only important for our dental health, but also for our general health.
An imbalance in the oral microbiome, on the other hand, can weaken our immune system and lead to digestive and even cardiovascular disorders. Modern medicine is therefore much more concerned with supporting the microbiome rather than sterilising it. As chlorhexidine has been proven to reduce the diversity of bacteria, create a more acidic environment and reduce nitrite availability, experts advise against the daily and long-term use of chlorhexidine - especially if the patient has a healthy oral microbiome.
Other side effects of chlorhexidine mouthwashes
In addition to disrupting the microbiome, chlorhexidine can have some - quite literally - unpleasant side effects: Long-term use can lead to tooth discolouration, as chlorhexidine adheres particularly well to the teeth and can easily bind to dye molecules from black tea, coffee & co. In addition, there may be temporary changes in the sense of taste during treatment. In some cases, chlorhexidine can slow down wound healing or trigger allergic reactions such as skin irritation, redness, burning and, in very rare cases , an anaphylactic reaction.
Application: In which situations is chlorhexidine still useful?
Despite the side effects listed, chlorhexidine still has an important place in dentistry due to its high effectiveness.
In the following situations, the use of chlorhexidine is still considered the gold standard for the short-term prevention of plaque formation:
- After dental surgery (for example, after wisdom tooth surgery or the insertion of implants)
- For acute inflammation in the mouth (e.g. as a mouthwash for gingivitis , periodontitis , peri-implantitis , peri-implant mucositis or in the case of a secondary infection)
- For patients who are unable to clean their teeth after an operation due to disability, old age or bedriddenness
It is important that you follow your dentist's instructions and do not use the mouthwash with chlorhexidine for longer than prescribed.
Good to know:
The products in the Perio plus range from Curaprox not only contain chlorhexidine, but also Citrox®. These bioflavonoids from bitter orange enhance the antibacterial effect.
How do you use chlorhexidine mouthwashes correctly?
Mouthwashes with chlorhexidine vary in their CHX concentration from 0.05 to 0.2 per cent and can therefore be used for different lengths of time. Please follow your dentist's instructions regarding the duration of use.
How to use a mouthwash with chlorhexidine:
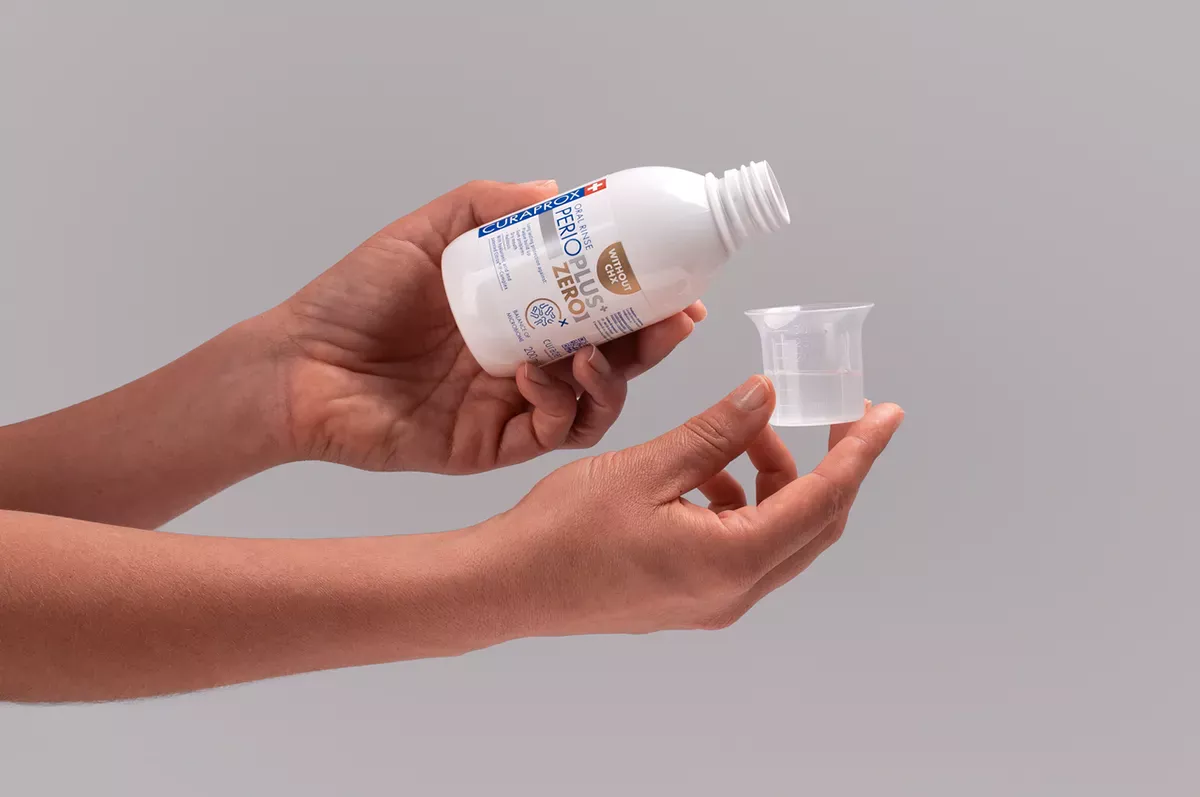
- Rinse your mouth with 10 millilitres of mouthwash for 60 seconds in the morning and evening
- Then spit it out - please do not swallow!
- Do not dilute the mouthwash
- Keep away from children
- For oral use only
This example is based on a mouthwash with a CHX concentration of 0.2 %. The maximum duration of use here is seven days.
Good to know:
The Perio plus zero mouthwash from Curaprox does not contain chlorhexidine and, with its patented Citrox®/P complex and other active ingredients, helps to effectively combat gum problems, plaque formation, bad breath and dry mouth - without any side effects. It is suitable for long-term use.
Frequently asked questions about chlorhexidine
Do mouthwashes with chlorhexidine help with toothache?
Toothache is often caused by tooth decay and chlorhexidine is an effective agent to kill bacteria responsible for tooth decay. However, if you have a toothache, you should visit your dentist or dental hygienist, as further treatment may be necessary.
Can mouthwashes with chlorhexidine be used during pregnancy?
To date, there is insufficient information on chlorhexidine during pregnancy and breastfeeding. It should therefore only be used with particular caution and after consultation with your dentist.
Can fluoride toothpaste be used together with chlorhexidine mouthwash?
Yes, but the two dental care products should not be used directly after each other. Chlorhexidine can react with certain ingredients in fluoride toothpaste - for example with sodium lauryl sulphate (SLS) or fluoride salts - which can lead to reduced effectiveness.
Can chlorhexidine be used daily in the long term?
Dentists do not recommend using chlorhexidine mouthwashes over a longer period of time, as this can lead to tooth discolouration, altered taste sensation and irritation of the mucous membrane. Chlorhexidine mouthwashes should only be used according to the instructions of a dentist.
Is chlorhexidine mouthwash suitable for children?
Chlorhexidine mouthwashes can be used on children, but only under the guidance and supervision of a healthcare professional. Care must be taken to ensure that the child does not accidentally swallow the mouthwash.
Is there an alternative to chlorhexidine mouthwashes that has no side effects and is suitable for long-term use?
Yes, Perio plus zero from Curaprox is a gentle yet effective alternative to CHX mouthwashes that does not contain chlorhexidine and is suitable for long-term use. With its patented Citrox®/P complex and other active ingredients, it effectively helps to combat gum problems, plaque formation, bad breath and dry mouth - without any side effects.
Sources:
Albrecht, Kerstin: Researchers advise more cautious CHX use in patients with a healthy microbiome, on: zm-online.de.
Bescos, Raul et al: Effects of Chlorhexidine mouthwash on the oral microbiome, in: Scientific Reports. 2020.
Federal Institute for Drugs and Medical Devices: Chlorhexidine: Anaphylactic reactions.
Curaprox: Perio plus zero. Details of laboratory studies.
DocCheck Flexikon: Chlorhexidine.
Fraunhofer: But with milk, please: Choice of drinks during chlorhexidine treatment.
Yellow list: Chlorhexidine.
Rehberg, Carina: Camomile tea: Effect and application, on: zentrum-der-gesundheit.de
Giessen University Hospital: Causes of tooth decay.
Van Strydonck, Daniëlle et al: Effect of a chlorhexidine mouthrinse on plaque, gingival inflammation and staining in gingivitis patients: a systematic review, in: Journal of Clinical Periodontology.
All websites last accessed on 23/05/2025.
 Swiss premium oral care
Swiss premium oral care